Fasteners on cars are used to hold various components and parts together. They come in a variety of types, sizes, and materials, such as bolts, nuts, screws, clips, and rivets. Fasteners are essential for ensuring that parts of the car remain securely attached and do not come loose while driving. They are typically made of steel, stainless steel, or aluminum to provide strength and durability. Fasteners are used throughout the vehicle, including in the engine, chassis, body panels, interior components, and suspension system. Proper installation and maintenance of fasteners are crucial for the safety and performance of the vehicle.

1. Overview of automotive fasteners
Automotive fasteners are important components in vehicles that hold parts together. They play a vital role in ensuring the structural integrity, safety and performance of your vehicle. Here are some key points about automotive fasteners:
1.1 Fastener Types
There are many types of automotive fasteners, including bolts, nuts, screws, clips, rivets, washers and pins. Each type of fastener is designed for the specific application and requirements of the vehicle.
1.2 Materials :
Automotive fasteners are typically made from high-strength materials such as steel, stainless steel, aluminum and titanium. The materials used in fasteners are selected based on factors such as strength, corrosion resistance, and weight.
1.3 Applications :
Fasteners are used in a variety of components and systems throughout the vehicle, including the engine, transmission, chassis, body panels, interior, suspension and exhaust systems.
1.4 Importance of Proper Installation :
Proper installation of automotive fasteners is critical to the safety and performance of your vehicle. Over-tightening or over-tightening fasteners can lead to problems such as component failure, leaks, and structural damage.
1.5 Maintenance and Replacement :
Regular inspection and maintenance of fasteners is important to ensure they remain safe and in good condition. Damaged or worn fasteners should be replaced promptly to prevent potential problems.
1.6 Torque specifications :
Automakers provide specific torque specifications for fasteners to ensure they are tightened to the correct level. It is recommended to use a torque wrench to obtain proper torque and prevent over-tightening.
1.7 Specialty Fasteners :
Some automotive applications require specialty fasteners such as self-locking nuts, flange bolts, captive fasteners. These specialized fasteners are designed to meet specific requirements for vibration resistance, sealing or accessibility.
2. Threaded fasteners
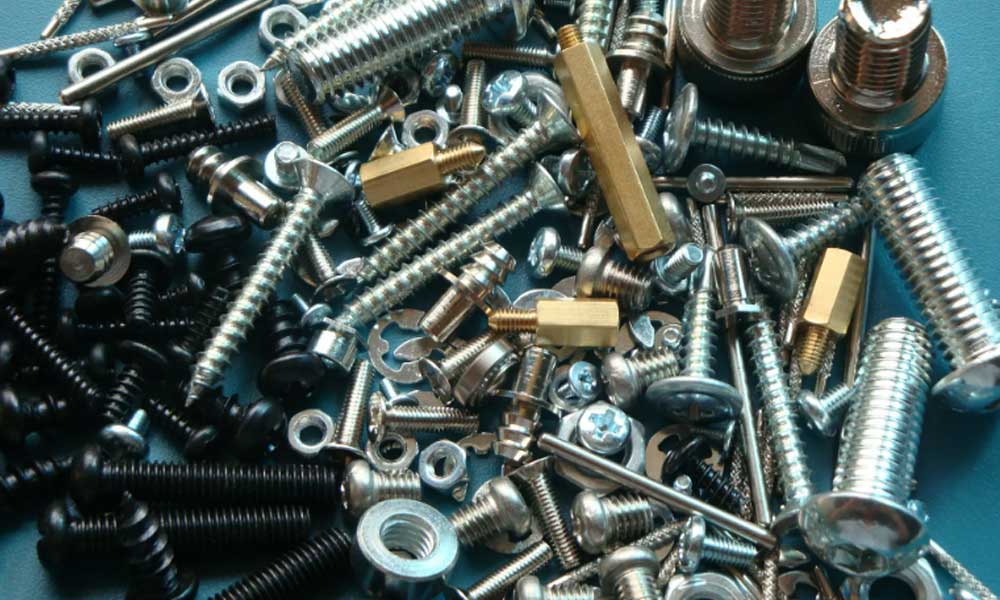

The most common fasteners for automobile parts are as shown in the figure. The force caused on the bolt when tightening the bolt and the force acting on the fastened part is the clamping force. Commonly used thread standards are metric (metric) threads. A small number of imported cars from the United States and the United Kingdom may use inch threads (UNC, UNF). In addition, some sensors and screw plugs on vehicles also use cylindrical pipe threads and conical pipe threads.
2.1 Strength level identification:
The ISO metric bolt strength grade label consists of two parts of numbers, which represent the nominal tensile strength value and the yield strength ratio of the bolt material. For example, the bolt of grade 4.8 means that the tensile strength of this bolt is 400MPa; the yield strength ratio of the bolt material is 0.8, and the yield strength is 400x 0.8=320MPa.
The meaning of bolt strength grade is an internationally accepted standard. Bolts of the same performance grade, regardless of whether their materials and origins are the same, as long as they have the same performance, can be replaced with the same performance grade. Switching to weaker bolts can easily break, stronger bolts are not always safe, and stronger bolts tend to be more brittle, may fail in certain applications, and are more expensive. The grade markings on the nuts are the same as those on the bolts.
3. Optimization of automotive fastener varieties and materials
With the continuous development of the automobile industry, in order to curb the increase in production, management and other costs caused by the increasing number of automobile fasteners, various automobile manufacturers have benchmarked and optimized fasteners from four aspects: structural elements, materials, heat treatment and surface treatment. .
The types of automotive fasteners are optimized and divided into: bolts, screws, nuts, threads, and washers.
Hexagonal flange face bolts are recommended first, and the use of hexagonal head bolts, hexagonal head bolts + spring washers, hexagonal head bolts + spring washers + flat washers, and hexagonal head bolts + flat washers is restricted.
As the requirements for assembly efficiency are also constantly increasing, hexagon socket screws are preferred, the standard structure is optimized, and the use of hexagon socket screws and cross-recessed screws are gradually restricted.
If the structure permits, hexagonal flange nuts are preferred. For parts with special anti-loosening requirements, consider using effective torque lock nuts, such as all-metal lock nuts and non-metal insert lock nuts. Because the load-bearing capacity and anti-loosening ability of fine threads are higher than that of coarse threads, when selecting larger-sized threaded fasteners, you should try to choose fine threads, and at the same time, you can reduce the variety of threaded fasteners.

4. Surface treatment of automotive fasteners
Automotive fasteners include bolts, nuts, and washers. Most of them must undergo surface treatment to protect them from corrosion, improve their appearance, or achieve certain special functions.
As environmental protection gradually tightens, the use of trivalent chromium passivation, zinc-aluminum coating and other more environmentally friendly methods for automotive fasteners is the future trend. Chromate passivation film is exposed to an environment above 70°C for a long time and is anti-corrosion. Performance will be compromised, so galvanized passivation should be used with caution in areas with higher ambient temperatures.
The zinc-aluminum coating has no hydrogen embrittlement and meets environmental protection requirements. The coating colors are black and gray. Bolts with grade 10.9 and above are preferred. The adhesion strength between the zinc-aluminum coating and the substrate is not as good as that of zinc plating, and the powder may fall off during use. Therefore, it cannot be used inside transmission components, and it is not recommended for bolts that need to be repeatedly disassembled.
Compared with zinc plating, the anti-corrosion ability of zinc-nickel alloy is greatly improved. After passivation and sealing treatment, it can also meet the requirements of high temperature resistance.
The melting point of copper is around 1083 C. In high-temperature environments, in order to avoid sintering of threaded parts, copper plating is chosen for surface treatment, especially for automotive fasteners around engine exhaust manifolds.

Overall, automotive fasteners are critical components that play a vital role in the construction, assembly, and maintenance of vehicles. Proper selection, installation and maintenance of fasteners are critical to ensuring the safety, reliability and longevity of your vehicle.





